Translate this page into:
Bloody blanket over the bone
*Corresponding author: Ganesh S. Dharmshaktu, Department of Orthopedics, Government Medical College, Haldwani, Uttarakhand, India. drganeshortho@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Dharmshaktu GS, Pangtey T. Bloody blanket over the bone. J Musculoskelet Surg Res 2023;7:310-2.
HISTORY
A 16-year-old girl presented with traumatic pain and swelling of the right thigh for 2 days, with pain medications providing transient relief. She had a history of transfusion-dependent hemophilia. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the affected extremity was done.
What are the radiographic findings?
What is the diagnosis?
What are three common differential diagnoses?
FINDINGS
There is a hyperintense collection around the bone extending from the distal femoral physis and extending up to a large segment of diaphysis proximally [Figures 1 and 2]. The thickness of the collection surrounding the bone is more pronounced posteriorly [Figure 3]. Besides it, the distal meta-diaphyseal area of the femur shows discrete patches of intramedullary infarcts.
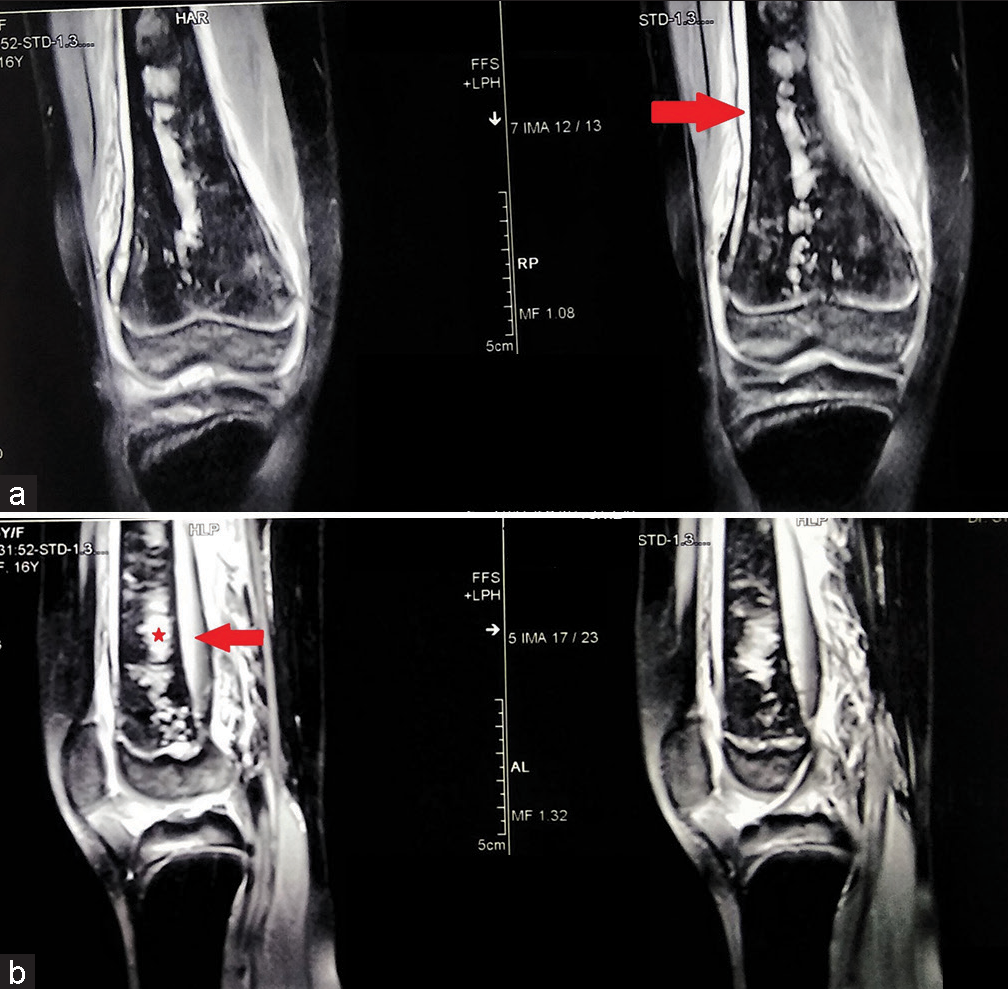
- The magnetic resonance imaging coronal images show the hyperintense collection in the subperiosteal region (red arrow) extending from the distal femoral physis to the proximal diaphysis (a). The collection is large and more pronounced (red arrow) posterior to the distal femur (b). There are areas of medullary infarcts (denoted by a red star) involving the meta-diaphysial region.
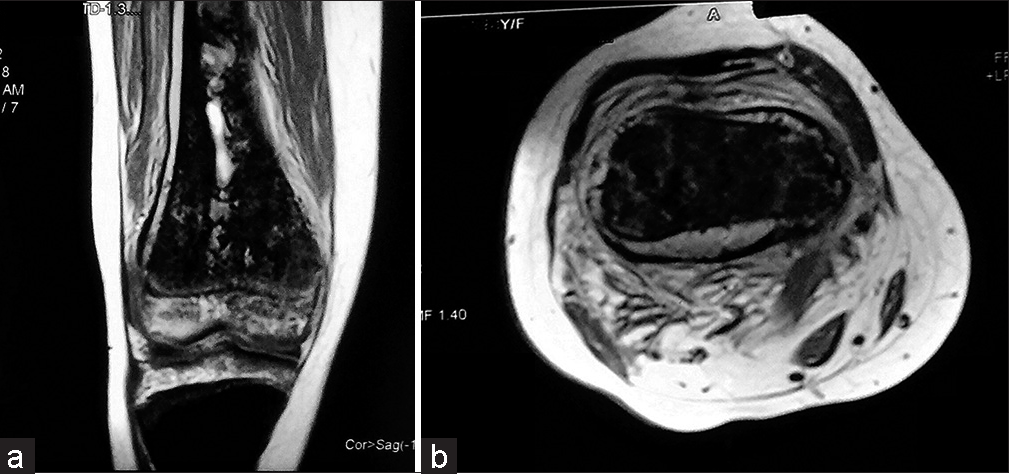
- The magnetic resonance imaging coronal T1-weighted (a) and axial (b) images show hyperintense collection in the subperiosteal region and areas of increased intensity within medullary infarcts.
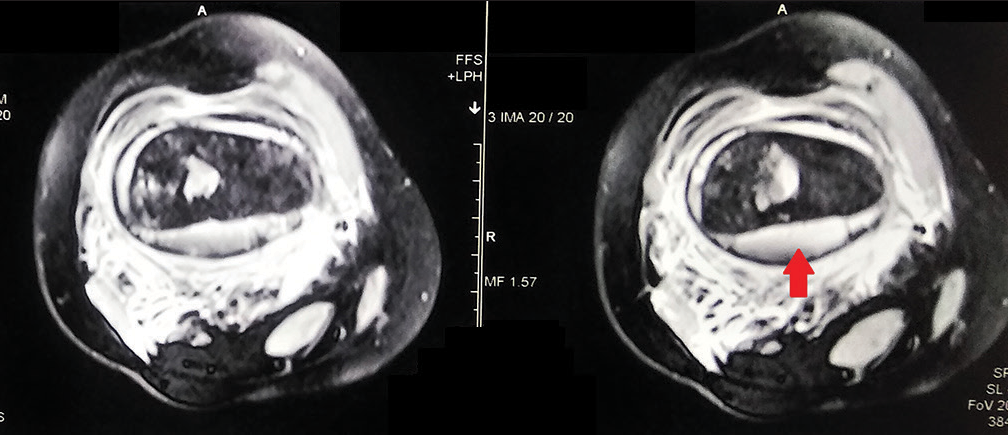
- The magnetic resonance imaging axial fat-suppressed sections show the more posterior collection (red arrow) surrounding the bone.
DIAGNOSIS
Large sub-periosteal hemorrhage along with medullary bone infarct.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Important common differential diagnoses are as follows:
Infection (acute osteomyelitis)
Ewing sarcoma
Bone infarct
Lymphoma/blood cell tumors
PEARLS AND DISCUSSION
Hemophilia is an inherited condition causing deficiency of clotting factors VIII or IX factor, causing hemophilia A and B, respectively (A more frequent than B). Serum concentration of factors determines mild, moderate, and severe types of the disorder. Hemorrhage from spontaneous or mild traumatic events is common and bleeding in osteoarticular tissues is also found.[1] Full-blown fractures or dislocations further complicate the problem and pose treatment challenges requiring various bleeding control strategies.[2]
Acute osteomyelitis is an important mimicker that should be ruled out with associated clinical features such as fever, raised temperature, or swollen extremities. The relevant blood tests such as increased leukocytes, neutrophils, and acute phase reactants like C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be helpful. Besides, subperiosteal collection (abscess) takes time to develop and is seldom seen so early in the course of the disease.
Ewing’s sarcoma may often mimic features of acute osteomyelitis clinically and radiologically. Both may have pain, fever, and elevated inflammatory markers. There is also the presence of cortical destruction and periosteal reaction in Ewing’s sarcoma. Careful differentiation in MRI is required to differentiate between the two followed by biopsy confirmation.[3]
Bone infraction results from vascular supply compromise and local ischemia, leading to aseptic necrosis of bone. These are more commonly encountered in sickle-cell disease.[4] Medullary infarction features include variable medullary calcification and new bone formation at the corticomedullary junction. Bone infarct, however, in a few cases may complicate into osteomyelitis as medullary infarct may function as sequestra and, thus, predispose to further infection.[5] Various sorts of lymphomas are also reported and are rare differentials.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
TP did the literature search and wrote the first draft while GSD collected the data. All authors have critically reviewed and approved the final draft and are responsible for the manuscript’s content and similarity index.
DECLARATION OF PATIENT CONSENT
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient’s parent has given his consent for the patient’s images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The parent understands that the patient’s name and initials will not be published, and due efforts will be made to conceal the identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There are no conflicting relationships or activities.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY FOR MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT AND SPONSORSHIP
This study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
References
- Hemophilia-related radial head re-dislocation. J Musculoskelet Surg Res. 2020;4:52-5.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Distinguishing osteomyelitis from Ewing's sarcoma on radiography and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;205:640-50. quiz 651
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone marrow infarction in sickle cell anaemia: Correlation with hematologic profiles. Blood. 1982;60:1411-9.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Osteomyelitis originating in and around bone infarcts: Giant sequestrum phenomena. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:387-91.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]